Exercises with Python grader utils¶
This chapter includes exercises that utilise the Python-grader-utils framework, which is recommended if you are creating Python exercises.
In this exercise you must implement a function hello
that returns a string "Hello Python!".
The following is an example of a graderutils exercise, where the problem is to implement a simple prime number checker primes.is_prime.
An incorrect solution can be found in primes.py, which is compared against the reference solution model.py.
Run the tests to get test results in JSON (use develop mode to generate all errors and warnings):
python3 -m graderutils.main test_config.yaml --develop-mode > results.json
Convert the JSON results into HTML:
cat results.json | python3 -m graderutils_format.html --full-document > results.html
You can now view results.html in a browser.
If you don't want to render the base template, you can omit --full-document. This renders only the feedback body using the default feedback template.
In this exercise, you must implement the function is_prime
that returns True if the argument (integer) is a prime number,
False otherwise.
Paths to custom Jinja2 HTML templates that extend or replace the default template at graderutils_format/templates/feedback.html can be defined in the test_config.yaml as follows:
feedback_template: my_feedback_template.html
A+ presents the exercise submission form here.
The following example shows how to embed arbitrary JavaScript into the feedback template, and make data from grader tests available for the scripts.
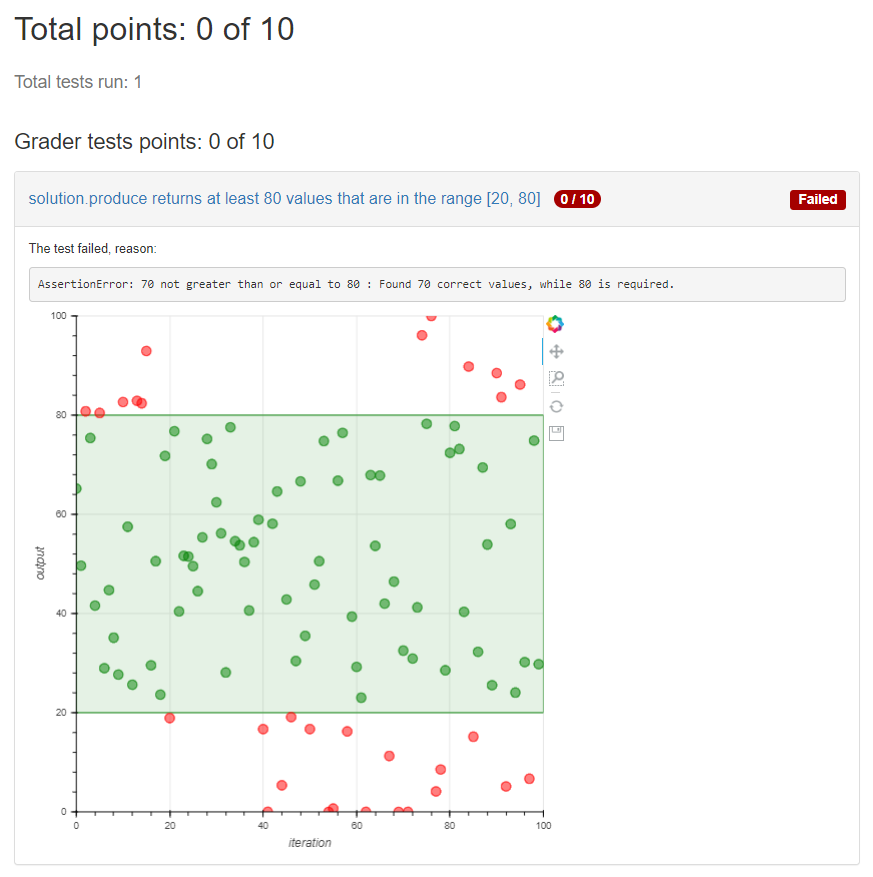
Notice that this exercise uses the Docker container image
apluslms/grade-python:math-3.13-5.0-4.13 because it includes the plotting library Bokeh.
You can submit the file solution_wrong.py to see the feedback.
IOTester¶
Input and output of a program can be compared against the input and output of a model program by using the test methods provided by IOTester, which is part of Graderutils.
IOTester can be used to feed inputs and/or parameters to a program/function. The output of the
student program and model program are captured and compared in different ways depending on
the used tests (text_test, numbers_test, etc.) and colored feedback showing the differences
is given. Google's diff_match_patch is used for the detection and coloring of the differences.
Tools for testing things like return values and classes/objects are also available, among
other things.
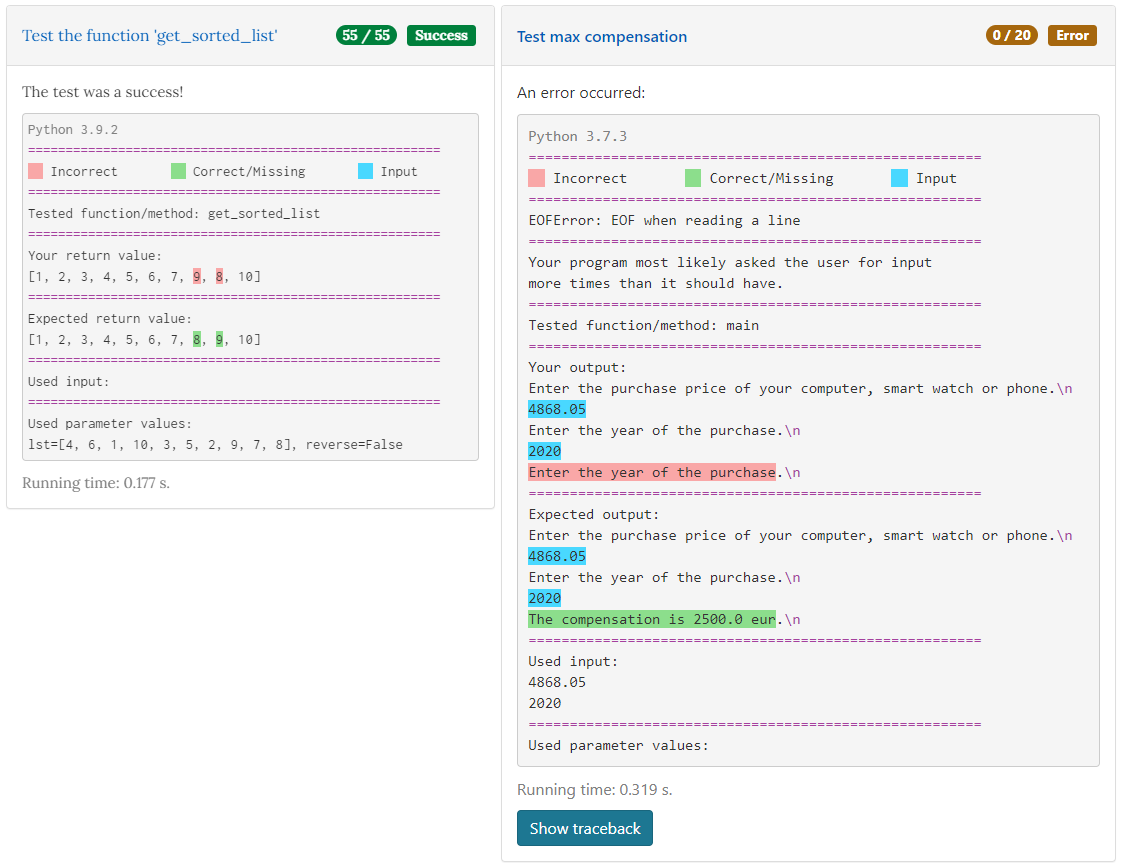
List of useful tests/tools¶
text_test
Run the model program and the student program and compare the text outputs. Ignore numbers, whitespace and characters specified in
self.settings["ignored_characters"].Parameters:
func_name(default:"")Name of the function to be tested. This is shown in the feedback.
If
func_nameis an empty string, the program is imported and the code on the module-level is executed. If the program contains functionmain()but it has not been called, the test fails with an error messageFunction main() was found but it was not called. Make sure that you remember to call the main() function and that the function call is correctly indented.args(default:())Tuple or list of positional arguments that are passed to the function with name
func_name. This is shown in the feedback.kwargs(default:{})Dictionary of keyword arguments that are passed to the function with name
func_name. This is shown in the feedback.inputs(default:[])List of strings that are fed to the program as input when prompted. This is shown in the feedback.
Each string acts as if the user would have typed it on a keyboard and pressed Enter. To simulate a user not typing anything and only pressing Enter, import and use the
ENTERconstant fromIOTesteras the input string.prog(default:None)Function that is run instead of a Python module. This is useful in cases where you want to do something before/after running the function that is being tested. For example, if the student submits a Python class, you might want to create an instance of the class with some specific initial values and then call one of the object's methods to see if it returns the correct value.
Note that when using a
progfunction,func_nameis shown in the feedback as the name of the function that was tested,argsandkwargsare shown as the used parameter values, andinputsis shown as the used input. This is so that the functionprogcan have its ownprog_args,prog_kwargsandprog_inputsthat are hidden and possibly different thanargs,kwargsandinputsthat are shown in the feedback.prog_args(default:())Tuple or list of positional arguments that are passed to the function
progif it is defined.prog_kwargs(default:{})Dictionary of keyword arguments that are passed to the function
progif it is defined.prog_inputs(default:[])List of strings that are fed to the function
progif it is defined.desc(default:"")String with a custom description/hint for the test. This is shown in the feedback.
compare_capitalization(default:False)Boolean variable stating if capitalization differences in the output should trigger an
AssertionErroror not.
numbers_test
Run the model program and the student program and compare the numbers in the outputs. Ignore everything except numbers. Match integers, decimals and numbers such as +1, 2e9, +2E+09, -2.0e-9.
Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
func_name(default:"")args(default:())kwargs(default:{})inputs(default:[])prog(default:None)prog_args(default:())prog_kwargs(default:{})prog_inputs(default:[])desc(default:"")compare_formatting(default:False)Boolean variable stating if formatting differences in the numbers should trigger an
AssertionErroror not. For example, 0.750 vs 0.75 and 0005 vs 5.
return_value_test
Run a function from the model program and the student program and compare the return values of the two functions.
Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
func_name(default:"")args(default:())kwargs(default:{})inputs(default:[])prog(default:None)prog_args(default:())prog_kwargs(default:{})prog_inputs(default:[])desc(default:"")show_output(default:False)Boolean variable stating if the output of the student program should be shown in the feedback. Showing the output might help students debug their program.
complete_output_test
Run the model program and the student program and compare the text, numbers and whitespace. Ignore characters specified in
self.settings["ignored_characters"].Parameters are identical to text_test:
func_name(default:"")args(default:())kwargs(default:{})inputs(default:[])prog(default:None)prog_args(default:())prog_kwargs(default:{})prog_inputs(default:[])desc(default:"")compare_capitalization(default:False)
no_output_test
Run the student program and test that nothing is printed.
Parameters (already explained earlier):
func_name(default:"")args(default:())kwargs(default:{})inputs(default:[])prog(default:None)prog_args(default:())prog_kwargs(default:{})prog_inputs(default:[])desc(default:"")
created_file_test
Run the model program and the student program and compare the data in the file they create. The data in the two files has to be identical. This test fails with an error if the student program does not create a file with the correct name specified by parameter
file_name(see below).Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
file_name(required)Name of the file that the student program and model program should create. This is shown in the feedback.
func_name(default:"")args(default:())kwargs(default:{})inputs(default:[])prog(default:None)prog_args(default:())prog_kwargs(default:{})prog_inputs(default:[])desc(default:"")
random_state_test
Run the model program and the student program and compare Python's pseudo-random number generator states. Used to test a function that sets random seed and to check that a program generates pseudo-random numbers the correct amount of times.
Parameters (already explained earlier):
func_name(default:"")args(default:())kwargs(default:{})inputs(default:[])prog(default:None)prog_args(default:())prog_kwargs(default:{})prog_inputs(default:[])desc(default:"")
amount_of_functions_test
Test that the student program contains the required amount of functions.
NOTE:Breaks if graderutils flag--use-rpycis used in config.yaml and the student's Python module contains custom classes.Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
op(required)One of the following strings:
">","<",">=","<=","=="This specifies the operator used for the comparison. For example, with
">"asopand2asamountthe test will pass if the student program contains more than two functions.amount(required)Integer that the number of found functions is compared against using operator
op.desc(default:"")
class_structure_test
Create an instance of the model class and the student class and compare the structure of the classes and objects.
NOTE:Breaks if graderutils flag--use-rpycis used in config.yaml.Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
class_name(required)Name of the class to be tested. This is shown in the feedback.
args(default:())Tuple or list of positional arguments that are used to initialize an instance of class with name
class_name. This is shown in the feedback.kwargs(default:{})Dictionary of keyword arguments that are used to initialize an instance of class with name
class_name. This is shown in the feedback.checks(default:[])List containing strings (see below), which specify the tests performed on the class structure.
"object_attrs": Check required instance/object attributes exist and that they are of the correct type"class_attrs": Check required methods, functions and variables exist in the class and that they are of the correct type"no_extra_object_attrs": Check that no extra instance/object attributes are found"no_extra_class_attrs": Check that no extra methods, functions or variables are found in the classdesc(default:"")
class_init_test
Create an instance of the model class and the student class by running their
__init__()functions and compare the values assigned to the objects' attributes. The output of__init__()can also be tested in different ways by setting the corresponding parameters toTrue.NOTE:Breaks if graderutils flag--use-rpycis used in config.yaml.Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
class_name(required)Name of the class to be tested. This is shown in the feedback.
args(default:())Tuple or list of positional arguments that are used to initialize an instance of class with name
class_name. This is shown in the feedback.kwargs(default:{})Dictionary of keyword arguments that are used to initialize an instance of class with name
class_name. This is shown in the feedback.run_text_test(default:False)Run text_test on
__init__()if set toTrue.run_numbers_test(default:False)Run numbers_test on
__init__()if set toTrue.run_complete_output_test(default:False)Run complete_output_test on
__init__()if set toTrue.run_no_output_test(default:False)Run no_output_test on
__init__()if set toTrue.compare_capitalization(default:False)compare_formatting(default:False)desc(default:"")
class_str_call_test
Test that an object's
__str__()method is not called directly, i.e., check thatprint(obj)is used instead ofprint(obj.__str__()).Parameters:
object_name(required)Name of the object that is used in the feedback text if the test fails.
feedback
Return a decorator for displaying better feedback than just the
AssertionErrormessage or traceback. Do not call otherIOTestertests inside a method that has been decorated with this. Can be used to improve the feedback of a normal test method that does basic assertion tests.Parameters (some of these already explained earlier):
func_name(default:"")Only used for showing in the feedback.
args(default:())Only used for showing in the feedback.
kwargs(default:{})Only used for showing in the feedback.
inputs(default:[])simple(default:False)Produce more simple feedback if set to
True.show_used_inputs_and_params(default:False)Show
inputs,argsandkwargsin the feedback if set toTrue.message(default:"")Override the default feedback hint message with a custom one.
The default message is
Your program did not pass the assertion (comparison) of values.if parametersimpleis set toFalseandYour program did not pass this test.if parametersimpleis set toTrue.desc(default:"")
model_directory
Context manager for moving to the model directory so that model modules can be imported in test methods that use the feedback decorator. Use together with feedback decorator in unit tests that need to manually use model.
Settings¶
In order to use IOTester one must first create an instance of IOTester. This is done in the
beginning of the unit tests in the following way:
iotester = IOTester()
Optionally, a dictionary of settings can be passed as parameter settings.
Below you can see the default settings that IOTester uses.
DEFAULT_SETTINGS = {
# Maximum amount that floating-point numbers are allowed to differ (+-)
# in submission output/return value and model output/return value
"max_float_delta": 0.02,
# Maximum amount that integer numbers are allowed to differ (+-)
# in submission output/return value and model output/return value
"max_int_delta": 0,
# Maximum student/model program execution time in seconds (integer)
"max_exec_time": 30,
# Characters that should not trigger an AssertionError when comparing outputs
"ignored_characters": ['.', ',', '!', '?', ':', ';', '\''],
# Libraries that are allowed to be imported. Use list ['*'] to whitelist all libraries.
"import_whitelist": [
"collections",
"copy",
"csv",
"datetime",
"decimal",
"functools",
"itertools",
"math",
"numbers",
"random",
"re",
"statistics",
"string",
"time",
],
# Libraries that are not allowed to be imported. Use list ['*'] to blacklist all libraries.
"import_blacklist": [],
# Files that are allowed to be opened. Use list ['*'] to whitelist all files.
"open_whitelist": [],
# Files that are not allowed to be opened. Use list ['*'] to blacklist all files.
"open_blacklist": ['*'],
}
For example, you can override the default max_float_delta setting value of 0.02 with 0.01 if
you initialize IOTester as below:
# Only max_float_delta setting will be changed. Other settings will stay as defaults.
iotester = IOTester(settings={"max_float_delta": 0.01})
The settings can also be changed later, for example, inside test methods. However, note that the settings will change for all the subsequent test methods as well, so you should reset them at the start of the other test methods, if you only wish to have different settings for one specific test.
# Overwrites some or all of the current settings with the provided settings.
# Automatically verifies that the settings are of the correct type etc. by doing assertions.
iotester.update_settings({"max_exec_time": 60})
# Directly edit the current settings. Does not verify that the settings will work correctly.
iotester.settings["ignored_characters"].remove('?')
Generating data files¶
Random-generated data files must be created in a specific directory so that IOTester can find
find them and allow the student program to read them (and also because the exercise directory is on
a read-only file system). The below code is an example of how you can generate data files:
import os
import random
from graderutils.graderunittest import points
from graderutils.iotester import IOTester, ENTER, generated_path
...
with open(os.path.join(generated_path, "file.txt"), "w") as f:
for i in range(10):
f.write("{:d}\n".format(random.randint(1, 100)))
...
@points(10)
def test_01_return_value(self):
"""Test return value of function 'read_file'"""
iotester.return_value_test(func_name="read_file", args=["file.txt"])
Example exercises using IOTester¶
In this exercise, dice are rolled using Python's pseudo-random number generator. The program asks the user for input and it outputs the results of the dice rolls. The results are also saved into a CSV file.
Used tests/tools:
text_test
numbers_test
return_value_test
complete_output_test
no_output_test
created_file_test
random_state_test
amount_of_functions_test
You can submit the files solution_*.py to see the feedback generated by IOTester in
different scenarios.
In this exercise, a class Wallet (wallet.py) is returned along with a program that uses
it (wallet_program.py).
The program asks the user for input and it creates two Wallet objects and calls their methods
outputting the results after.
Used tests/tools:
text_test
numbers_test
return_value_test
no_output_test
class_structure_test
class_init_test
class_str_call_test
feedback
model_directory
You can submit the files solution_*_wallet.py and solution_*_wallet_program.py to see the
feedback generated by IOTester in different scenarios. There are also some examples of the
feedback decorator that show how it can provide better feedback for generic unit test methods
that don't call IOTester test functions.